Green hydrogen is coming - and these Australian regions are well placed to build our new export industry

Green hydrogen offers us a zero emissions way to transport enregy
In summary
You might remember hearing a lot about green hydrogen last year, as global pressure mounted on Australia to take stronger action on climate change ahead of the COP26 Glasgow summit last November. Analysis for The Conversation by Dr Steven Percy, Swinburne University of Technology.
The government predicts green hydrogen exports and domestic use could be worth up to A$50 billion within 30 years, helping the world achieve deep decarbonisation.
But how close are we really to a green hydrogen industry? And which states are best placed to host it? My research shows that as of next year, and based on where the cheapest renewables are, the best places to produce green hydrogen are far north Queensland and Tasmania.
As ever more renewable energy pours into our grid, this picture will change. By the end of the decade, the north Queensland coast could become the hydrogen powerhouse. By 2040, dirt-cheap solar should make inland areas across New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria and South Australia the lowest cost producers.
Renewable energy you can store and transport
Why is there so much buzz around green hydrogen? In short, because it offers us a zero emissions way to transport energy. Take cheap renewable energy and use it to split water into hydrogen and oxygen using an electrolyser. Store the hydrogen on trucks, ship it overseas, or send it by pipeline. Then use the hydrogen for transport, manufacturing or electricity production.
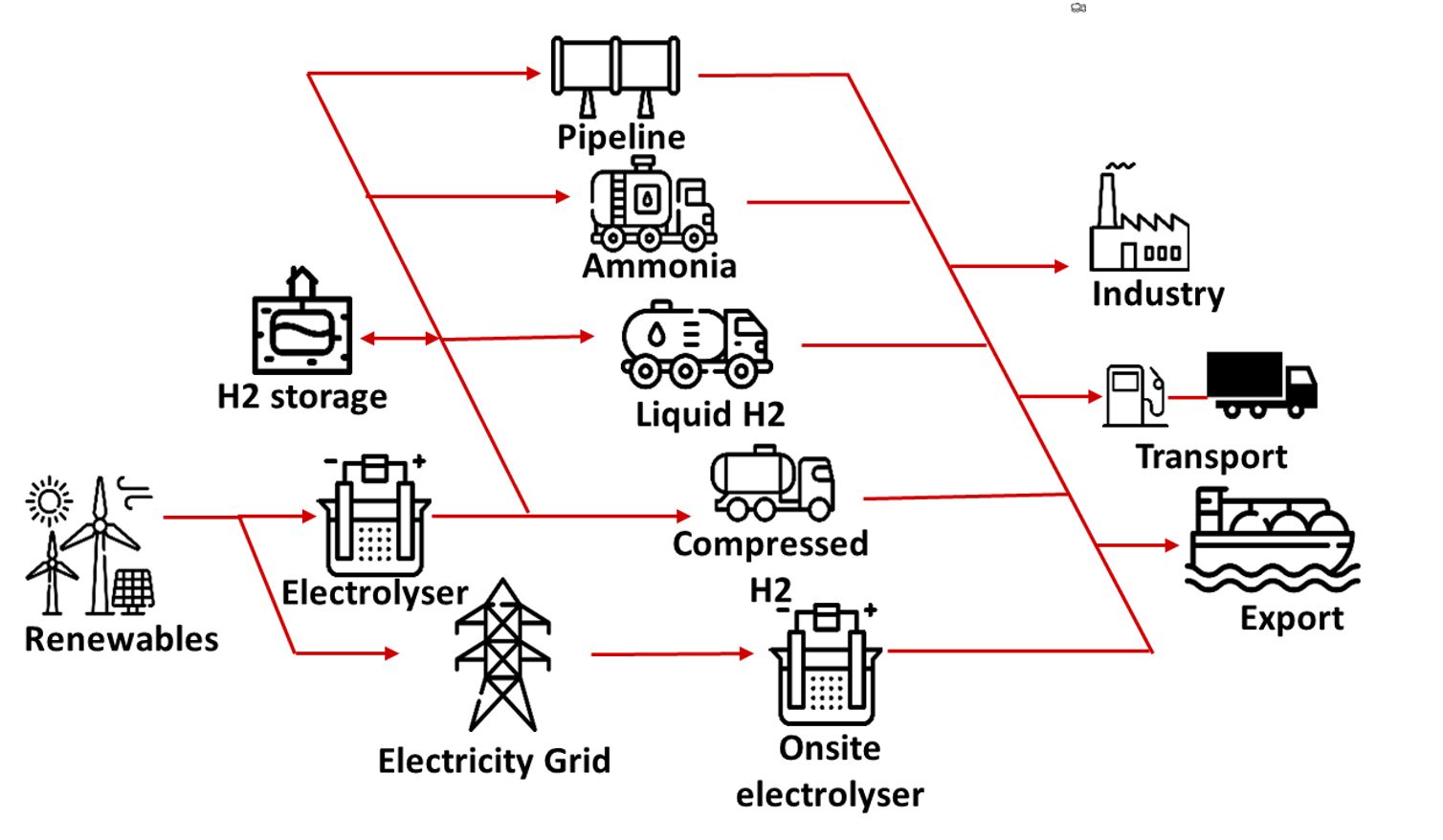
All the technology exists – it’s the cost holding the industry back at present. That’s where Australia and its wealth of cheap renewable energy comes in.
Making hydrogen is nothing new – it has a long history of use in fertiliser production and oil refining. But until now, the main source for hydrogen was gas, a fossil fuel.
In the last few years, however, there has been a sudden surge of interest and investment in green hydrogen, and new technology pathways have emerged to produce cheap green hydrogen. As global decarbonisation gathers steam, Japan, South Korea and parts of Europe are looking for clean alternatives to replace the role fossil fuels have played in their economies.
Australia is exceptionally well placed to deliver these alternatives, with world-beating renewable resources and ports set up for our existing fossil fuel exports, such as coal and LNG.
In 2019, we sold almost $64 billion of black coal, with most going to Japan, South Korea, India and China. As these countries decarbonise, the coal industry will shrink. Green hydrogen could be an excellent replacement.
How competitive is Australian hydrogen?
At present, Australia is a long way from producing green hydrogen cheap enough to compete with fossil fuels, given we seem to have no appetite for taxing carbon pollution.
Does that mean it’s a non-starter? Hardly. It was only a decade ago sceptics ridiculed solar and wind as too expensive. They’ve gone awfully quiet as renewable prices fell, and fell, and fell – as tracked by the International Renewable Energy Agency. Now renewables are cheaper than coal. Battery storage, too, has fallen drastically in price. The same forces are at work on the key technology we need – cheaper electrolysers.
By 2040, the CSIRO predicts an 83% fall in electrolyser costs, according to its Gencost 2021-22 report. By contrast, gas-derived hydrogen with carbon capture is predicted to reduce in cost only slightly. That means green hydrogen is likely to capture much of the market for hydrogen from 2030 onwards.
Which states could benefit?
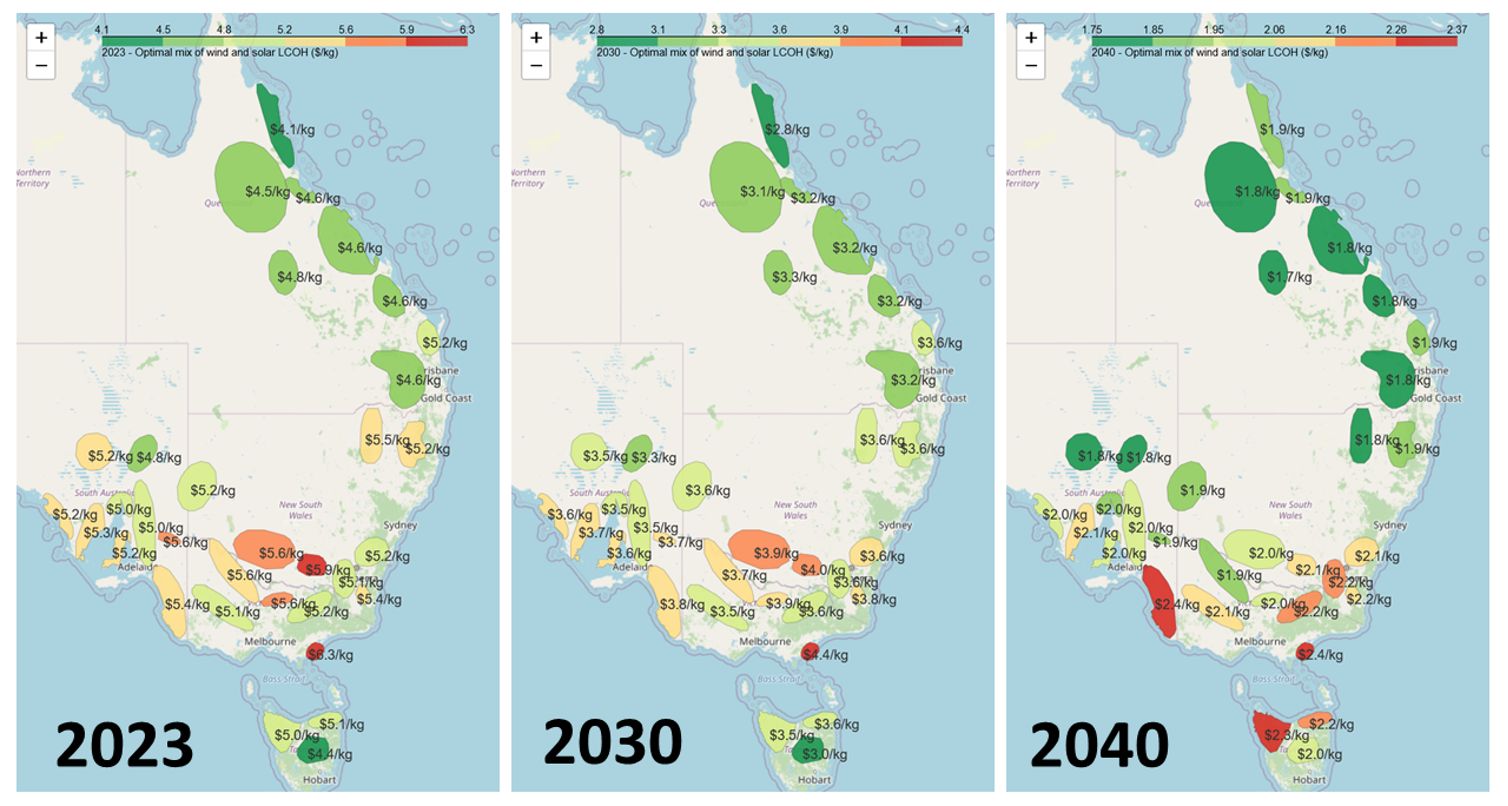
My research with the Victorian Hydrogen Hub) shows as of next year, the lowest cost location for green hydrogen would be Far North Queensland ($4.1/kg) and Tasmania ($4.4/kg) due to high renewable resources.
But this picture will change. By 2030, northern Queensland’s coastal regions could be the Australian hydrogen powerhouse due to a combination of cheap solar and access to ports. Western Australia and the Northern Territory could also have similar advantages, though the modelling for these areas has not yet been done.
As solar energy and electrolyser costs continue to fall, new states could enter the green hydrogen economy. In CSIRO’s cost predictions, electricity from solar is predicted to become much cheaper than wind by 2040. This means sunny areas like central and northern Queensland ($1.7/kg) and inland NSW, Victoria and South Australia ($1.8/kg) could be the best locations for green hydrogen production.
In making these estimates, I do not consider supply chain and storage infrastructure required to deliver the hydrogen. Transport could account for between $0.05/kg to $0.75/kg depending on distance.
Comparing my modelling to price thresholds set out in the National Hydrogen Strategy indicates we can produce green hydrogen for trucking at a similar cost to diesel within four years. Fertiliser would take longer, becoming competitive by 2040.
Does our dry country have the water resources for green hydrogen?
If we achieved the $50 billion green hydrogen industry the government is aiming for, how much water would it consume? Surprisingly little. It would take only around 4% of the water we used for our crops and pastures in 2019-20 to generate an export industry that size – 225,000 megalitres.
Much more water than this will be freed up as coal-fired power stations exit the grid. In Queensland and NSW alone, these power stations consume around 158,000 megalitres a year according to a 2020 report prepared for the Australian Conservation Foundation. Coal mining in these two states takes an additional 224,000 megalitres.
As the cost of renewable energy falls and falls, we will also be able to desalinate seawater along our coasts to produce hydrogen. We estimate this would account for only about 1% of the cost of producing hydrogen, based on Australian Water Association desalination cost estimates.
How can we get there faster?
This decade, we must plan for our new hydrogen economy. Government and industry will need to develop and support new hydrogen infrastructure projects to produce, distribute, use and export hydrogen at scale.
We’re already seeing promising signs of progress, as major mining companies move strongly into green hydrogen.
Now we need governments across Australia to rapidly get optimal policy and regulations in place to allow the industry to develop and thrive.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article
-
Media Enquiries
Related articles
-

- Technology
- Science
- Engineering
Victorian students drive green energy transition through international hydrogen competition
Swinburne’s KIOSC, in collaboration with Horizon Educational and Gippsland Tech School, co-hosted the Hydrogen Grand Prix in Melbourne.Friday 26 July 2024 -

- Science
Skin, scales and fish tails: using collagen to turn fish guts into gold
New research from Swinburne could transform the sector by converting high value collagen proteins from seafood by-products into cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals.
Tuesday 02 July 2024 -

- Science
- Engineering
Submarines in the future could self-identify cracks and self-heal thanks to Swinburne researcher
Thanks to the work of Dr Nisa Salim from Swinburne University of Technology’s School of Engineering, future submarines could self-identify microcracks and self-heal using a new kind of carbon fibre reinforced polymer composites.
Monday 17 June 2024 -

- Science
Inaugural Swinburne-CSIRO Indigenous Research Fellow joins national water quality forecasting project
Swinburne University of Technology has appointed spatial ecologist Associate Professor Sally Waller as its inaugural Swinburne-CSIRO Indigenous Research Fellow...
Thursday 13 June 2024 -

- Sustainability
Expert opinion: Nuclear power has ‘merits’, but investing in renewables ensures long-term energy security
The opposition is promising to build seven nuclear power stations but a Swinburne expert says it's possible to transition our energy system without relying on nuclear power.
Wednesday 19 June 2024

